







Many organizations today rely on preventive software and automation to keep cybersecurity threats at bay. Unfortunately, it’s just not enough to keep hackers away.
Human error and exploited vulnerabilities make network breaches a matter of when more than a matter of if. Cybersecurity experts fight a losing game when they focus solely on prevention.
Hackers bypass preventive tools every day. They add new tricks to their skill sets, and as hacking becomes easier, cybersecurity becomes more difficult (but far more critical). You have to know exactly what to search for to ensure that hackers have a hard time slipping through the cracks undetected.
The first goal of any hacker is to gain access to the network or machine. While automated systems like firewalls and antivirus software are good at keeping most malicious activity out, hackers are persistent and determined. They have many tricks up their sleeve. They’re skilled at evading preventive security measures to lay the foundations that will open the door for their black hat activities.
One technique they use is persistence. Attackers create persistent footholds as a way to maintain their access across restarts and reboots. It’s usually their first goal after initial access.
Getting that access usually makes a lot of digital noise. This is easy to spot if a network or endpoint is being monitored. Instead, hackers will abuse legitimate applications and processes to slip through the back door undetected. And once they’re inside, they establish a quiet foothold and plan their next move.
Hackers often use autorun files to establish a foothold. Autoruns start automatically when you power up your computer. Most autoruns are inherent to and necessary for your operating system. That’s what makes them the perfect hiding spot.
Once a hacker has access, they want to evade detection for as long as possible. The foothold files they install might not do anything right away, but they act as a stub for later payloads.
If your automated security scans it, it might not find anything suspicious. So, it will just move on, thinking it’s just a defunct or dormant file. This keeps it hidden from detection, but the actual malware is bundled up in layers and will still detonate inside your machine or network.
This is where automated threat detection fueled by human threat hunters provides the missing piece of the puzzle. Humans have the contextual awareness to pick up on the suspicious run keys, code, file extensions or any other shady tactics that automation-only tools might miss.
Watch the video below to hear from one of our human threat hunters how hackers are sneaking past automated security—and what you can do about it.
Protecting your IT environments generally means prevention, but you need more than prevention to fully protect you and your customers. You need to go full circle and adopt all five phases of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
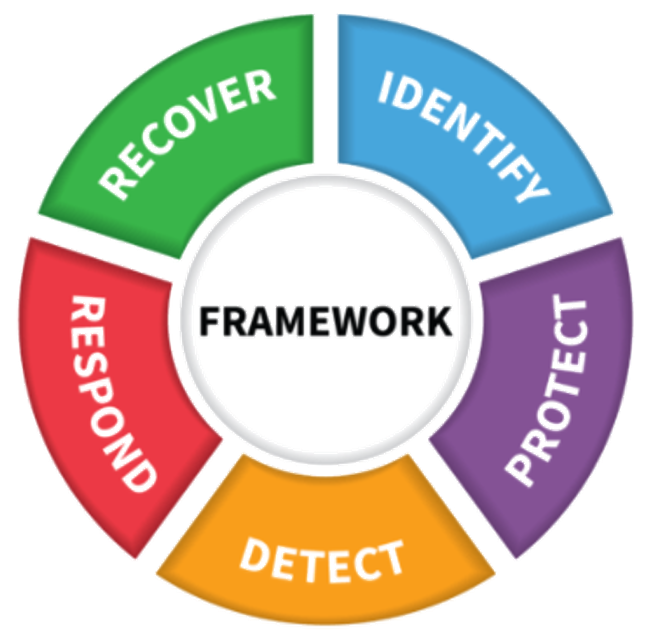
As you can see, a layered approach is foundational to guarding your SMB clients. But here’s the hard truth: hackers only have to find a single flaw to sneak in and implant their foothold. Then, they can secretly come and go as they please until they move to the exploitation or exfiltration phase.
To counter their hidden footholds and malicious autoruns, your security team needs threat hunters who specialize in managed detection and response. These skilled threat hunters can analyze, investigate, reverse engineer and uncover malicious activity that would otherwise have gone undetected.
The key to threat hunting is contextual awareness. Some forms of obfuscation or evasion techniques can easily slip past an automated solution. But a real human being can look for those breadcrumbs to flag suspicious files and programs while leaving required programs alone to do their job.
Huntress specializes in threat detection and response. Our SOC team focuses on rooting out footholds and ransomware because we believe they are the biggest threats to your protected environments. We also help you find external-facing vulnerabilities like hidden RDP services that are publicly accessible and close them down.
Our cybersecurity platform is specifically designed for MSPs and VARs who service SMBs. It includes the following methods of managed endpoint detection and response:
Ready to see the platform for yourself? Sign up for a free trial today.
Get insider access to Huntress tradecraft, killer events, and the freshest blog updates.
